The Arab League, officially called the League of
Arab States, is a regional organization of Arab states
in Southwest Asia, and North and Northeast Africa. It
was formed in Cairo on March 22, 1945 with six members:
Egypt, Iraq, Transjordan (renamed Jordan after 1946),
Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Syria. Yemen joined as a
member on May 5, 1945. The Arab League currently has 22
members.
The main goal of the league is to:
"draw closer the relations between member States and
co-ordinate collaboration between them, to safeguard
their independence and sovereignty, and to consider in a
general way the affairs and interests of the Arab
countries."
The Arab League is involved in political, economic,
cultural, and social programs designed to promote the
interests of its member states. It has served as a forum
for the member states to co-ordinate their policy
positions, to deliberate on matters of common concern,
to settle some Arab disputes, and to limit conflicts
such as the 1958 Lebanon crisis. The league has served
as a platform for the drafting and conclusion of many
landmark documents promoting economic integration. One
example is the Joint Arab Economic Action Charter which
sets out the principles for economic activities in the
region.
Each member state has one vote in the League Council,
while decisions are binding only for those states that
have voted for them. The aims of the league in 1945 were
to strengthen and coordinate the political, cultural,
economic, and social programs of its members, and to
mediate disputes among them or between them and third
parties. Furthermore, the signing of an agreement on
Joint Defense and Economic Cooperation on April 13, 1950
committed the signatories to coordination of military
defense measures.
The Arab league has played an important role in shaping
school curricula; advancing the role of women in the
Arab societies; promoting child welfare; encouraging
youth and sports programs; preserving Arab cultural
heritage and fostering cultural exchanges between the
member states. Literacy campaigns have been launched,
intellectual works reproduced, and modern technical
terminology is translated for the use within member
states. The league encourages measures against crime and
drug abuse, and deals with labor issues—particularly
among the emigrant Arab workforce.
Structure Arab League
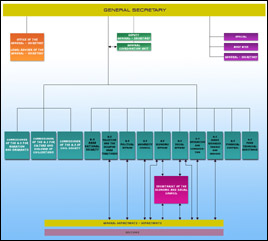
PDF File
|
Subsidiary Bodies of the Arab League |
| |
| |
|
1. Council |
|
|
(Internal Regulations of the
Council {1951})
&
(Internal Regulations of the Committees
{1951}) |
| |
|
|
S.No. |
Name of Committee |
| |
|
| A. |
Arab
Women's Committee |
| B. |
Committee of Arab Experts on Cooperation |
| C. |
Communications Committee |
| D. |
Conference of Liason Officers |
| E. |
Cultural Committee |
| F. |
Health Committee |
| G. |
Human
Rights Committee |
| H. |
Information Committee |
| I. |
Legal
Committee |
| J. |
Organization of Youth Welfare |
| K. |
Political Committee |
| L. |
Social Committee |
| M. |
Permanent Committee for Administrative
and Financial Affairs |
| |
|
|
| |
|
2. General Secretariat
|
| |
|
|
|
|
(Internal Regulations of the
Secretariat-General of the League
{1953}) |
| |
|
|
|
|
S.No. |
Designation |
Name |
Country |
| |
|
|
|
| A. |
Secretary-General |
Dr.
Ahmad Esmat abd al-Meguid |
Egypt |
| B. |
Asst.
Secretary-General for Administrative &
Financial Affairs |
Ahmad
Qadri |
|
| C. |
Asst.
Secretary-General for Economic Affairs |
Dr.
Yousef Abdel-Wahab Niemat Allah |
Saudi
Arabia |
| D. |
Assistant Secretary-General for
Information Affairs |
Dawo
Ali Siwedan |
Libya |
| E. |
Assistant Secretary-General for Arab
Affairs |
Assad
al-Assad |
Lebanon |
| F. |
Assistant Secretary-General for
International Affairs |
Adnan
Omran |
Syria |
| G. |
Assistant Secretary-General for Military
Affairs |
Muhammad Said ben Hassan el-Berqdar
|
Syria |
| H. |
Assistant Secretary-General for Social
and Cultural Affairs |
Mahdi
Mustafa al-Hadi |
Sudan |
| I. |
Assistant Secretary-General, Head of
Secretary-General's Office |
Ahmad
Ibrahim Abdel |
Egypt |
|
| |
|
3. Defense and Economic
Cooperation Bodies |
| |
|
|
S.No. |
Name of Body |
| |
|
| A. |
Arab
Unified Military Command |
| B. |
Economic Council |
| C. |
Joint
Defense Council |
| D. |
Permanent Military Commission |
|
| |
|
4. Arab Deterrent Force |
|
|
|
5. Other Institutions of the
League |
| |
|
|
S.No. |
Name of Institution |
| |
|
| A. |
Administrative Tribunal of the Arab
League |
| B. |
Arab
Fund for Technical Assistance to African
and Arab Countries (AFTAAAC) |
| C. |
Special Bureau for Boycotting Israel |
|
| |
|
6. Offices Abroad in Non-Member
States |
| |
|
|
|
S.No. |
Name Of Country |
Address |
| |
|
|
| A. |
Argentina |
Gorostiaga 2021, 1426 Buenos Aires |
| B. |
Austria |
Grimmelshauengasse 12, 1030 Vienna |
| C. |
Belgium |
106
Ave Franklin D. Roosevelt, 1050 Brussels |
| D. |
Brazil |
Shis-Qi 15, Conj. 7, Casa 23, 71600
Brasila, DF |
| E. |
Canada |
170
Laurier Ave. West, Suite 604, Ottawa K1P
5VP |
| F. |
Ethiopia |
P.O.
Box 5768, Addis Ababa |
| G. |
Germany |
Friedrich Wilhelm Str. 2A, 5200 Bonn 1 |
| H. |
Greece |
Martious St., Filothei, Athens |
| I. |
India |
A-137
Neeti Bagh, New Delhi 110-049 |
| J. |
Italy |
Piazzle delle Belle Arti 6, 00196 Rome |
| K. |
Japan |
1-1-12 Moto Asabu, Minato-ku, Tokyo 106 |
| L |
Kenya |
P.O.
Box 30770, Nairobi |
| M. |
Russia |
28
Koniouch Kovskaya, Moscow |
| N. |
Senegal |
41
Rue el-Hadji Amadou, Assane Ndoye, Dakar |
| O |
Spain |
Paseo
de la Castellana 180, 6o, Madrid 16 |
| P. |
Switzerland |
9 rue
de la Valais, 1202 Geneva |
| Q. |
U.S.A |
747
3rd Avenue, New York, NY 10017
1100- 17th Street, NW, Suite 901,
Washington, DC 20036
Additional offices in Chicago, Dallas,
and San Francisco |
|
(
website: http://www.arableagueonline.org )
Go to top
|